Disclaimer:
This article is intended for educational and research purposes only. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment guidance. AI-generated outputs should never be used for patient care or clinical decision-making. All information is presented in the context of technical evaluation, research, and educational discussion.
Information Sources: This article is based on publicly available research and official documentation:
- Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models (arXiv, 2023)
- Large Language Models Encode Clinical Knowledge (Nature, 2023)
- Google Cloud Vertex AI MedLM Documentation
Table of Contents
Med-PaLM 2: A Technical Overview
Image source: Google Research official blog (2023) | Used for educational purposes under Fair Use
Med-PaLM 2 is Google’s specialized large language model (LLM) designed for research and educational exploration in medical question-answering. Released in March 2023, it achieved high performance on structured medical benchmarks, reflecting its potential as a tool for technical evaluation and knowledge assessment rather than clinical practice.
Key benchmark results include:
- MedQA: 86.5% accuracy
- MedMCQA: 72.3% accuracy (Indian medical exam dataset)
Controlled evaluations suggested that the model can produce answers that align with authoritative reference materials and structured knowledge assessment scenarios. These results indicate the model’s effectiveness in research-oriented tasks, not in live clinical decision-making.
For detailed methodology and results, see the official research paper and Nature publication.
Development Background: From PaLM to Med-PaLM
Med-PaLM 2 builds on Google’s PaLM foundation models:
- PaLM: Trained on 780 billion tokens from a wide range of sources, including scientific literature, web content, and encyclopedias.
- PaLM 2: Enhanced multilingual reasoning and improved contextual understanding. Learn more about PaLM 2

Image source: Google AI Blog “Introducing PaLM 2” (2023) | Used for educational and research purposes under Fair Use
Med-PaLM 2 extends these models with medical fine-tuning and advanced prompting techniques:
- Ensemble refinement: Combines multiple reasoning paths to improve consistency.
- Chain of retrieval: Breaks answers into claims, retrieves relevant studies, and produces evidence-aligned outputs.
These methods are designed to reduce hallucinations and ensure outputs are consistent with research-backed knowledge, not for patient-specific guidance.
Training Data and Fine-Tuning
Instruction fine-tuning on medical datasets includes:
- MedQA
- MedMCQA
- HealthSearchQA
- LiveQA
- MedicationQA
The model focuses on technical understanding of medical knowledge rather than real-world patient interactions. This ensures it is appropriate for educational and research scenarios, where accuracy in structured datasets matters.
Performance and Technical Capabilities
Med-PaLM 2 demonstrates strong benchmark performance:
- MedQA: 86.5%
- PubMedQA: 81.8%
- Selected MMLU clinical topics: state-of-the-art results
Human evaluators in controlled research settings found the model’s answers to be well-structured and reference-aligned, useful for knowledge exploration, training simulations, and documentation research. These findings reflect technical utility, not clinical reliability.
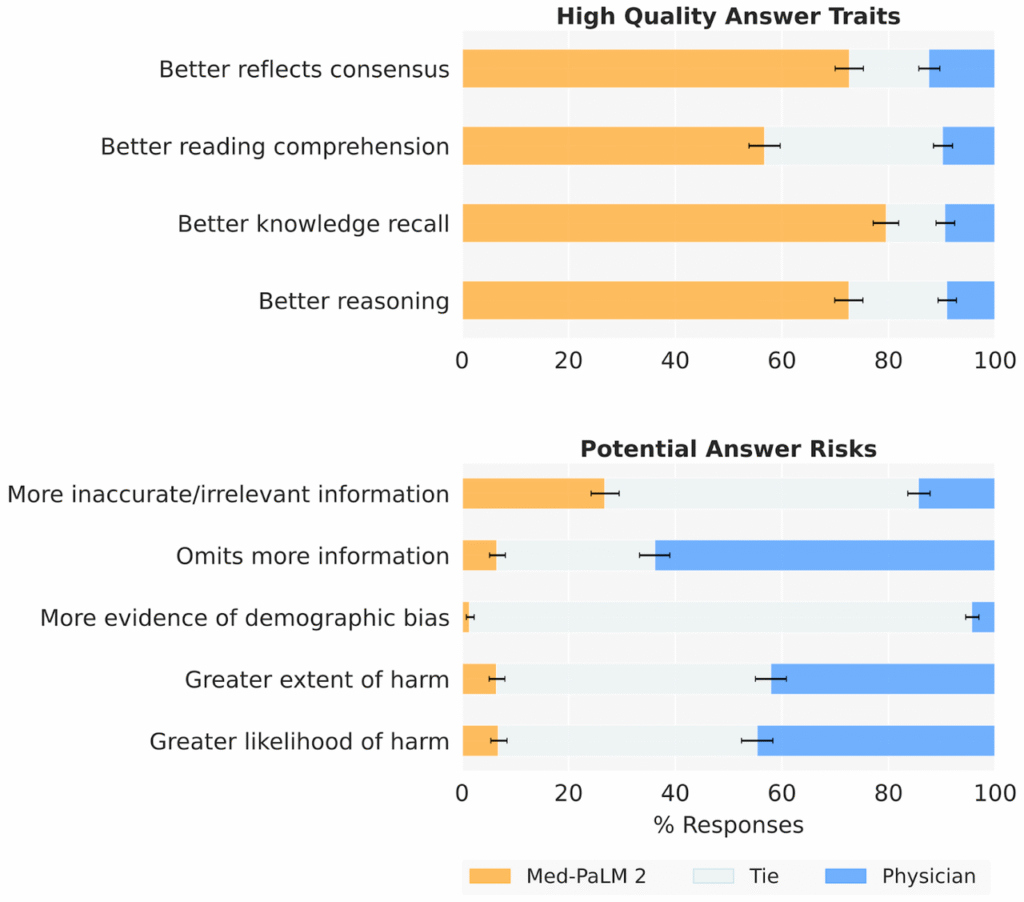
Image source: Singhal et al., arXiv:2305.09617 (2023), Figure 4 | Original research chart, used under Fair Use
Research-Oriented Use Cases
Med-PaLM 2 has been explored in research, documentation draft generation, and educational contexts, including:
- Summarizing research content for pre-clinical studies
- Producing structured educational exercises for medical knowledge evaluation
- Generating drafts for technical workflows that are always reviewed by qualified professionals
All real-world outputs in these use cases are subject to expert review, ensuring they are not used for diagnosis or treatment.
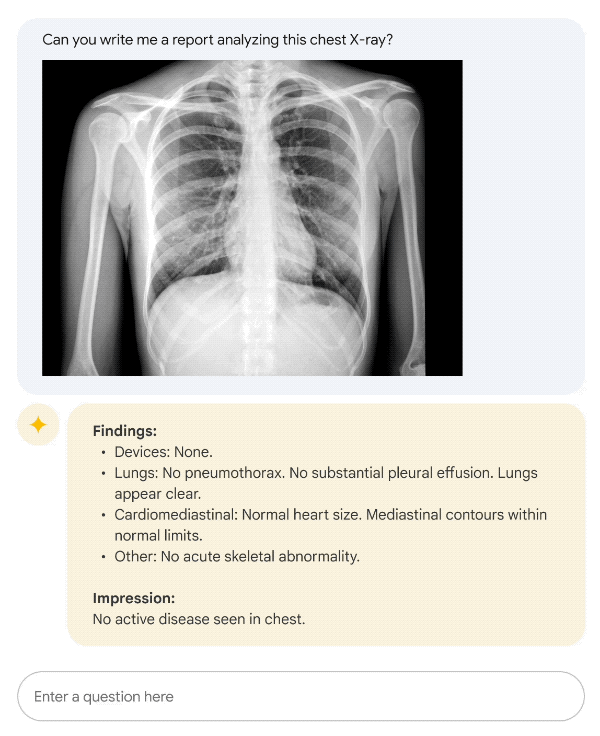
Image source: Google Research Med-PaLM 2 technical report or demo (2023) | Not a real clinical report — illustrative only, used under Fair Use for education
Limitations and Considerations
Despite strong benchmark results, the model has limitations:
- Hallucination risk: Outputs may appear plausible but be incorrect.
- Bias risk: Training data may introduce biases in answers.
- Benchmark vs. real-world: Performance on exams or datasets does not translate to clinical reliability.
- Regulatory status: Med-PaLM 2 is not a medical device and has no clinical approval.
Regulatory Context:
All applications must remain in research, educational, or technical evaluation contexts, with mandatory expert oversight.
Access and Technical Deployment
MedLM, the platform based on Med-PaLM 2, is available to select Google Cloud users for research purposes only. Key considerations:
- Outputs are drafts for evaluation
- Human oversight is required
- Data privacy standards must be maintained (e.g., HIPAA compliance if handling sensitive datasets)
The platform is not intended for patient-facing applications.
For technical specifications and access requirements, see MedLM Documentation.
Image source: Google Cloud Community public forum (May 2023) | Used under Fair Use for educational context
Future Directions in Medical LLM Research
Research is exploring multimodal capabilities, such as integrating text with imaging or genomic data. These developments remain experimental and are focused on scientific exploration and knowledge assessment.
Newer models, including Gemini-based variants fine-tuned for medical datasets, have achieved high performance on structured exams, but all outputs should be interpreted as research tools, not clinical guidance.
Conclusion
Med-PaLM 2 represents a significant advancement in medical AI research, achieving high accuracy on structured benchmarks and generating answers aligned with reference materials. Key takeaways:
- Research and educational tool only
- Mandatory human oversight for all outputs
- Not suitable for diagnosis or patient care
This model highlights the potential of AI to support knowledge assessment, research workflows, and educational applications in the medical domain without introducing clinical risk.
Reminder: All medical decisions must be made by licensed healthcare professionals. AI-generated outputs are research artifacts, not substitutes for professional medical judgment.
References and Further Reading
Primary Research
- Singhal, K., et al. (2023). “Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models.” arXiv:2305.09617. https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.09617
- Singhal, K., et al. (2023). “Large Language Models Encode Clinical Knowledge.” Nature, 620, 172–180. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06291-2
Official Documentation
- Google Cloud. “Vertex AI MedLM Documentation.” https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/medlm/medlm-prompts
Regulatory and Ethical Guidelines
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices.” https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-aiml-enabled-medical-devices
- World Health Organization. “Ethics and Governance of Artificial Intelligence for Health.” (2021) https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240029200
Additional Context
- Google AI. “Introducing PaLM 2.” https://ai.google/discover/palm2/
Image Copyright Notice:
All images in this article are sourced from Google Research, Google Cloud official blogs, Nature journal papers, or public community forums. They are used solely for educational and research purposes under the U.S. Fair Use doctrine.
For commercial use or redistribution, please obtain permission from the original copyright holder.
Information Currency Notice: This article reflects information available as of March 2023. Medical AI technologies and regulatory policies evolve rapidly. For the most current information, please consult the official sources listed above.
External Link Disclaimer: External links are provided for reference purposes only. The authors are not responsible for the content of external websites. Link availability and content may change over time.






