With the arrival of Google’s MedGemma, the field of healthcare AI has a powerful new open-source player. This analysis explores the diverse ecosystem of competitors, from flexible open models to integrated clinical platforms, defining the best alternatives for specific needs.
The year 2025 has marked a significant milestone in healthcare artificial intelligence with Google’s release of MedGemma, a family of open-source generative AI models built on the Gemma 3 architecture. Designed to comprehend both complex medical text and imaging data, MedGemma offers powerful capabilities for tasks like report generation and clinical reasoning . However, the landscape of medical AI is not monolithic. A vibrant ecosystem of alternatives has emerged, each with unique strengths, target audiences, and technological approaches. Choosing the “best” alternative requires a nuanced understanding of whether the goal is open-ended research, enterprise-wide clinical integration, or solving a specific departmental workflow challenge.
Table of Contents
1. The Context: Multimodality as the New Frontier in Medical AI
MedGemma’s core strength lies in its multimodality—the ability to process and synthesize information from different data types, such as text-based clinical notes and image-based X-rays or CT scans. This approach is redefining how AI is leveraged in medicine. As noted by researchers, humans are naturally multimodal, but are limited in the volume of data they can process. AI can overcome this by finding signals in the noise across vast, disparate datasets .
The value of this approach is quantifiable. A 2025 scoping review analyzing 432 papers found that multimodal AI models consistently outperform their unimodal counterparts, showing an average improvement of 6.2 percentage points in Area Under the Curve (AUC) metrics . While MedGemma is a prominent example, it is part of a broader trend, with numerous players developing solutions that integrate diverse data to enhance clinical decision-making.
2. Open-Source Competitors: For Flexibility and Customization
For developers and researchers who value transparency, control, and the ability to fine-tune models for specific tasks, the open-source community offers several compelling alternatives to MedGemma. While they may not always have the out-of-the-box medical specialization, their flexibility is a major asset.
Mistral Large
French AI startup Mistral AI has released powerful open-source models, with Mistral Large positioned as a top-tier competitor. It is lauded for its strong reasoning capabilities and native fluency in multiple languages, including English, French, German, and Spanish . Released under the permissive Apache 2.0 license, it is highly attractive for commercial applications. Its primary limitation as a MedGemma alternative is its current lack of native multimodality, focusing exclusively on text. However, for text-based tasks like analyzing clinical notes or medical literature, its large context window (up to 128k tokens) and reasoning skills make it a formidable option .
Meta’s Llama 3
Meta’s Llama 3 series has demonstrated performance that rivals or even surpasses proprietary models on certain benchmarks, particularly in reasoning and code generation . Like Mistral, Llama 3 is currently text-only, though Meta has indicated future versions will incorporate multimodality. For research institutions looking to build custom medical applications from a strong text-based foundation, Llama 3 offers a powerful and well-supported starting point.
Other Gemma Variants
It’s worth noting that Google itself provides a family of open models alongside MedGemma. Models like PaliGemma 2 (for visual language tasks) and CodeGemma (for code generation) can be considered alternatives for specific components within a larger healthcare AI system. While not tailored for medicine, they offer specialized capabilities that could complement a medical AI project.
3. Enterprise & Clinical-Grade Platforms: The Big Tech Players
For large healthcare organizations, a standalone model like MedGemma is only one piece of the puzzle. The greater need is often for integrated, compliant, and scalable platforms. Here, major technology companies offer comprehensive ecosystems that serve as powerful alternatives.
Microsoft’s Healthcare AI Ecosystem
Microsoft has made a significant push into healthcare with its Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare. A direct competitor to MedGemma’s imaging capabilities is **MedImageParse 3D**, a foundation model available in the Azure AI Foundry. It is specifically designed to handle complex 3D datasets from MRI and CT scans, enabling precise segmentation and analysis of anatomical structures . Microsoft’s strategy focuses on integration, allowing healthcare organizations to orchestrate multimodal AI insights directly within Microsoft Fabric, combining imaging data with clinical notes, sentiment analysis, and social determinants of health (SDOH) data to create a holistic patient view.
OpenAI’s Strategic Partnerships and Tools
OpenAI’s strategy is to provide powerful core models and foster an ecosystem of specialized, compliant tools built upon them. A prime example is **Doximity GPT**, which uses OpenAI’s models but adds a crucial HIPAA-compliant layer. It is designed to assist clinicians with administrative tasks like generating clinical documentation, summarizing patient charts, and drafting patient communications in multiple languages . This approach offers the power of models like GPT-4 within a secure clinical workflow. OpenAI’s direct initiatives, such as hiring a Doximity co-founder to lead its healthcare push and developing tools like HealthBench, signal a deepening commitment to becoming a “medical thought-partner” for clinicians .
4. Specialized AI Solutions for Clinical Workflows
Beyond general-purpose models and broad platforms, a category of alternatives focuses on solving specific, high-impact problems within clinical departments. These tools are often designed for seamless integration and immediate workflow benefits.
Aidoc: The Radiology Co-pilot
Aidoc offers a compelling alternative for radiology departments. Its AI-powered platform, the aiOS™, analyzes medical images (primarily CT scans) in real-time to detect and triage acute abnormalities like brain hemorrhages or pulmonary embolisms . Its key differentiator is a unified “;Widget” that consolidates AI results from various algorithms and vendors into a single interface within the radiologist’s existing workflow. This solves a major pain point of managing multiple AI tools. For a hospital looking to augment its radiology practice, Aidoc provides a more targeted and integrated solution than a general model like MedGemma .
Merative: For Large-Scale Data Analytics
Formerly IBM Watson Health, Merative represents an alternative focused on a different type of AI. Rather than generative tasks, Merative’s platform excels at descriptive and predictive analytics on vast quantities of clinical and patient data . Its use cases include analyzing population health data, optimizing treatment plans, and supporting clinical trials. For organizations focused on deriving insights from existing health records at scale, Merative’s analytics-driven approach offers a different, yet equally valuable, capability compared to MedGemma’s generative focus.
Dax Copilot: Ambient AI for Documentation
Nuance’s Dax Copilot, powered by Microsoft Azure OpenAI, targets one of the biggest sources of clinician burnout: administrative work. It is an ambient AI tool that automatically documents patient encounters by listening to voice conversations . By integrating with widely used electronic health record (EHR) platforms like Epic, it streamlines a critical but time-consuming task. This represents an alternative that focuses on operational efficiency rather than diagnostic support, complementing the capabilities of models like MedGemma.
5. Comparative Analysis: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The “best” alternative to MedGemma is entirely dependent on the user’s needs. The chart below visualizes the key differences between MedGemma and some of its top alternatives across four critical dimensions: openness, multimodality, clinical integration, and medical specialization.
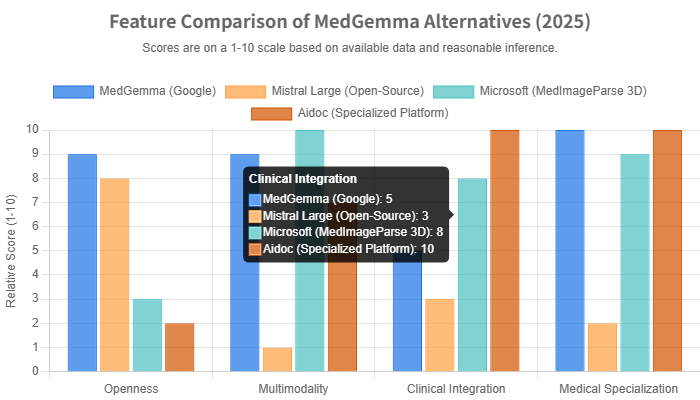
- Openness: MedGemma and Mistral Large lead as open models, offering high flexibility. Microsoft and Aidoc are proprietary platforms, prioritizing control and integration over open access.
- Multimodality: Microsoft’s MedImageParse 3D excels with its focus on complex 3D imaging. MedGemma is strong with 2D images and text. Aidoc is highly specialized in medical imaging, while Mistral is currently text-only.
- Clinical Integration: Aidoc is the clear winner here, with a platform built specifically to integrate into existing radiology workflows (PACS/EHR). Microsoft’s platform strategy also provides strong integration capabilities. MedGemma, as a base model, requires significant development work to be integrated.
- Medical Specialization: MedGemma and Aidoc are purpose-built for medical tasks. Microsoft’s MedImageParse is also highly specialized. Mistral Large is a general-purpose model that would require extensive fine-tuning for medical use.
Conclusion: A Diverse and Competitive Market
The launch of MedGemma has not created a winner-take-all scenario; rather, it has illuminated the diversity of needs within the healthcare AI market. There is no single “best” alternative, only the most appropriate choice for a specific context.
The decision hinges on a fundamental trade-off: Do you need a flexible, open-source foundation for research and development, or a fully integrated, compliant, and specialized tool for immediate clinical impact?
For developers and researchers, open-source models like **Mistral Large** offer powerful, flexible foundations, albeit without MedGemma’;s built-in medical multimodality. For large healthcare systems seeking enterprise-grade, compliant solutions, the integrated platforms from **Microsoft** and the specialized tools built on **OpenAI’s** models present a more direct path to deployment. And for specific departments aiming to solve a targeted workflow problem, specialized solutions like **Aidoc** for radiology or **Dax Copilot** for documentation deliver tangible, immediate value. The era of medical AI in 2025 is characterized by choice, and the emergence of strong competitors ensures that innovation will continue to accelerate across all fronts.






