When teams ask me about Epic AI scribe integration, they’re rarely looking for another glossy demo. They want to know: Can I ship this into production under HIPAA, keep clinicians safe from hallucinations, and actually reduce burnout without wrecking our change‑control process?
In this text, I’ll walk through how I approach Epic-integrated AI scribes from an engineering and clinical-safety lens, drawing on real deployments with ambient AI tools like Abridge, Suki, and Ambience Healthcare, and Epic’s own AI capabilities as of late 2025.
Medical & Regulatory Disclaimer (Updated December 2025)
This content is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or regulatory advice. Always consult your organization’s compliance, privacy, security, and clinical governance teams, and follow FDA, HIPAA/GDPR, and local regulations before deploying any clinical AI.
Table of Contents
Epic’s AI Strategy for EHR Integration
Epic has been very explicit about its AI posture: keep the system of record authoritative, keep humans in the loop, and make AI “feel invisible” inside existing workflows.
Exploring the Epic AI Marketplace for Clinical Tools
Epic exposes AI capabilities primarily through its AI Marketplace / Toolbox and Partners & Pals ecosystem. Instead of building every model in‑house, Epic vets and distributes external tools that plug into Hyperspace, Haiku, and Canto. You can explore Epic’s AI solutions for clinicians to understand their comprehensive approach.
From my experience with one large multi‑hospital system:
- Procurement insisted that every AI scribe come via an Epic-vetted route (e.g., Abridge as Epic’s first “Pal”) to simplify BAA, HIPAA risk assessment, and auditability.
- Technical teams benefited from standardized launch points (activity tabs, flowsheets, SmartLinks) instead of bespoke UI widgets.
Epic’s own documentation emphasizes a few consistent patterns:
- AI features are embedded where work already happens (note composer, In Basket, Haiku visit list).
- All AI output is draft‑only, requiring clinician review and attestation.
- Integrations must support comprehensive auditing, who recorded audio, which model generated which draft, and when edits were made.
Ambient AI Module: Enhancing Clinician Workflow
The core value of an Epic AI scribe integration is ambient capture during the encounter, especially for primary care, oncology, cardiology, and behavioral health.
A realistic example I’ve seen:
- A cardiologist launches an AI scribe from Haiku before entering the exam room.
- A secure audio stream captures the conversation (patient + clinician).
- Within ~30 seconds of visit end, a structured note appears in Epic: HPI, ROS, exam, assessment, and plan, mapped to the site’s note template.
- The clinician edits, signs, and the AI’s contribution is recorded in the audit log.
Well‑implemented ambient modules have consistently given clinicians 30–60 minutes back per day in the pilots I’ve helped run, but only when the integration feels native to Epic and doesn’t add extra clicks.
Epic AI Scribe Integration Architecture
At a high level, every Epic AI scribe integration I’ve deployed looks like the same three-box diagram: Epic ↔ secure integration layer ↔ AI scribe service.
API Connections: Secure Data Exchange with EHR AI
Most modern integrations use a combination of:
- FHIR R4 / USCDI APIs for problems, meds, allergies, vitals, lab results, and encounter metadata.
- Epic’s proprietary APIs / Interconnect for scheduling, encounters, and sometimes for pushing back fully composed notes.
- Eventing / webhooks (or Bridges/HL7 in older estates) to trigger AI processing when an encounter starts or ends.
A typical flow I’ve implemented:
- Haiku or Hyperspace launches the AI scribe with a context token (user, patient, encounter).
- The scribe service pulls minimal necessary clinical context via FHIR, under a BAA.
- Audio + metadata are processed by the vendor’s stack (often using a combination of proprietary ASR + LLM).
- The resulting draft is written back via:
- Note draft APIs, or
- SmartText / SmartPhrase injection into the existing note.
To reduce risk of hallucinations, I push vendors to:
- Clearly label inferred vs. explicitly stated content.
- Avoid pulling in out-of-encounter data unless the UI distinguishes it.
- Provide a diff view so clinicians can see what was added.
Epic Haiku Integration: AI Scribe on the Go
Mobile is where ambient AI shines. Haiku integration typically relies on:
- An in‑app recording control tied to the active patient/encounter.
- Background streaming of audio to the AI vendor over mutually authenticated TLS.
- A callback / polling mechanism so, when the note is ready, the clinician sees a badge or banner in Haiku and Hyperspace.
One outpatient clinic I worked with adopted a simple rule: “If you’re in the room, Haiku is open and the scribe is listening (with consent).” Documentation lag dropped from hours to minutes, and after the first month, over 80% of signed notes originated from AI drafts rather than blank templates.
Top Third-Party AI Scribes for Epic
As of 2025, three vendors dominate most Epic AI scribe conversations in my work.
Abridge Integration: Capturing Clinical Conversations Efficiently
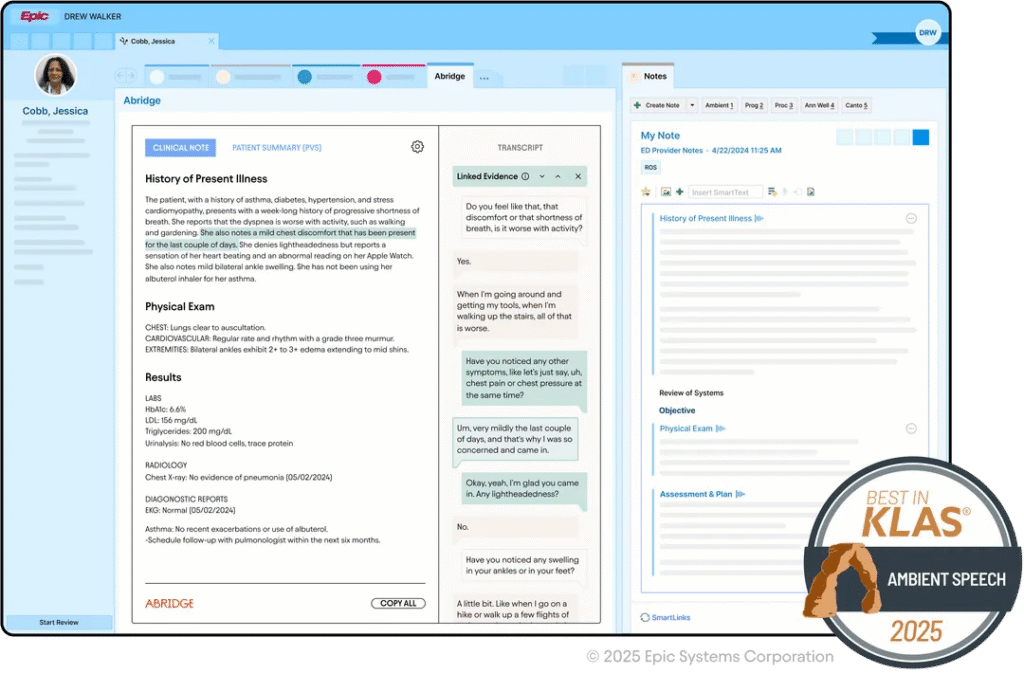
Abridge became Epic’s first Pal for generative AI charting, which matters from a governance standpoint: the integration pattern is well‑documented and battle‑tested across systems like UPMC and John Muir.
In practice, the Abridge ↔ Epic integration gives you:
- Deep ambient capture with visit‑type-aware note structures.
- Rapid draft notes in Epic, often within a minute of visit end.
- Tight Haiku integration plus Epic Toolbox deployment options.
I’ve found Abridge particularly strong in complex multisystem visits (e.g., oncology + comorbidities), though clinicians still need to watch for subtle misattribution of which specialist manages which issue.
Suki Integration: Streamlining Notes and Documentation
Suki’s Epic integration leans into voice-first workflows, think “Hey Suki, update the problem list” plus ambient scribing.
From a technical standpoint, I appreciate that Suki exposes clear boundaries between:
- What’s sourced from Epic (facts), and
- What’s synthesized by the model (narrative).
That separation makes it easier for me to design hallucination monitoring: I can periodically compare structured data against generated assessment/plan sections to catch risky divergences.
Ambience Integration: Real-Time Ambient Clinical Support
Ambience Healthcare’s Epic Toolbox integration focuses on real-time support inside Epic and Haiku: not just note drafting, but also in‑workflow suggestions. Learn more about Ambience Healthcare’s platform.
In one pilot I supported, Ambience produced:
- A near‑final SOAP note in Epic.
- Inline prompts reminding clinicians to address quality metrics (e.g., depression screening) if they came up in the conversation but weren’t charted.
The upside is obvious, better completeness and quality. The risk is subtle over‑reliance, so we explicitly trained clinicians to treat these as prompts, not orders.

Technical Implementation for Epic AI Scribes
Setup Requirements: System Prerequisites and Configurations
On the Epic side, I always confirm early:
- Interconnect / FHIR enabled with the right scopes.
- Access to Epic Toolbox / App Orchard / Connection Hub entries for the chosen vendor.
- Network paths from Haiku devices to the vendor endpoints via VPN or private peering.
On the vendor side, I insist on:
- Regional data residency options for HIPAA/GDPR.
- Configurable PHI retention windows and deletion workflows.
- Support for per‑site configuration (note templates, specialty-specific styles).
A small but important lesson: configure per‑department feature flags. I’ve had ED leadership delay adoption because they didn’t want recording enabled by default in behavioral health rooms.
Authentication and Security Best Practices for EHR AI
Security is where many pilots stall, and rightly so. My baseline requirements:
- OIDC/OAuth2 SSO tied to the organization’s IdP, with role-based access reflecting Epic user roles.
- Mutual TLS between Epic integration services and the AI vendor.
- Full audit logging for access to audio, transcripts, and drafts.
For higher‑risk specialties (psychiatry, substance use), I also recommend:
- Disabling long‑term audio retention by default.
- Periodic red‑team prompts to test for model leakage or unsafe suggestions.
And always: no training on local PHI unless you have explicit legal, ethics, and patient‑facing consent for that use.
Deployment Best Practices in Clinical Settings
Pilot Programs: Testing AI Scribes Before Full Rollout
My preferred pattern is a 6–12 week pilot:
- Start with 15–30 motivated clinicians across 2–3 specialties.
- Run a 2‑week “shadow mode” where AI drafts are generated but not used for final notes.
- Compare encounter timestamps, note completion times, and error rates against baseline.
We once caught a subtle issue, ambiguous abbreviations in orthopedics, only because we had a shadow period and a structured review rubric.
Clinician Training: Ensuring Effective Adoption
I’ve stopped thinking of this as “training” and more as co‑design. What works best:
- 30‑minute live demos inside their real Epic environment.
- Clear guidance on what not to trust (e.g., medication changes inferred from conversation).
- Specialty-specific tips (how the AI handles multi‑problem visits, family history, etc.).
Without this, adoption plateaus as clinicians revert to free‑texting everything they don’t fully trust.
Patient Consent: Managing Privacy and Trust
Consent is non‑negotiable. My go‑to safeguards:
- Clear signage and a verbal script: “I’m using an AI scribe that records our conversation to help with my notes. You can say no.”
- Easy opt‑out toggles in Haiku/Hyperspace.
- Logic to disable recording for sensitive parts of the visit (e.g., pelvic exams, specific counseling segments).
If a patient shows any discomfort, I instruct clinicians to immediately stop recording and revert to manual notes. That’s both ethically sound and critical for long‑term trust.
Measuring ROI and Success
Adoption Metrics: Tracking Usage and Engagement
For Epic AI scribe integration, I track three core metrics monthly:
- Active user rate: % of eligible clinicians using the scribe at least weekly.
- Encounter coverage: % of eligible visits where recording was used.
- Time-to-sign: median time from encounter close to signed note.
For one internal medicine pilot, time‑to‑sign dropped from 9.5 hours to 1.8 hours over eight weeks, with 70% encounter coverage, strong enough to justify expansion. For more insights on healthcare technology adoption, visit KLAS Research.
Documentation Quality: Evaluating Accuracy and Efficiency
I measure quality on three fronts:
- Accuracy: blinded reviews of AI-assisted vs. manual notes by senior clinicians, with scoring for clinical correctness and attribution of actions.
- Completeness: alignment with internal documentation standards and external quality measures (e.g., depression screening, vaccine status).
- Clinician experience: burnout and satisfaction scores, plus free‑text feedback on when the AI helped or hindered.
In one real case, psychiatry chose not to adopt the scribe broadly because, even though the notes were accurate, the clinicians felt it changed the tone of sensitive conversations. That’s a successful outcome too: the integration surfaced its own limits.
Disclaimer:
The content on this website is for informational and educational purposes only and is intended to help readers understand AI technologies used in healthcare settings.
It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, treatment, or clinical guidance.
Any medical decisions must be made by qualified healthcare professionals.
AI models, tools, or workflows described here are assistive technologies, not substitutes for professional medical judgment.
Deployment of any AI system in real clinical environments requires institutional approval, regulatory and legal review, data privacy compliance (e.g., HIPAA/GDPR), and oversight by licensed medical personnel.
DR7.ai and its authors assume no responsibility for actions taken based on this content.
Epic AI Scribe Integration FAQs
What is Epic AI scribe integration and how does it work in clinical workflows?
Epic AI scribe integration connects Epic to an ambient AI scribe via a secure integration layer. Clinicians launch the scribe from Hyperspace or Haiku, audio is streamed securely, the AI generates a draft note mapped to local templates, and the clinician reviews, edits, and signs inside Epic with full audit logging.
How does Epic AI scribe integration help reduce clinician burnout and documentation time?
Well-implemented Epic AI scribe integrations capture visits ambiently and return structured draft notes within about a minute of visit end. Pilots described in the article showed clinicians regaining 30–60 minutes per day and cutting time-to-sign from many hours to under two, when the workflows felt native and minimized extra clicks.
What security and HIPAA safeguards are required for Epic AI scribe tools?
Core safeguards include a signed BAA, minimal necessary PHI exchange over mutually authenticated TLS, Epic-aligned OIDC/OAuth2 SSO, and comprehensive audit logs for audio, transcripts, and drafts. Organizations should enforce configurable PHI retention, regional data residency, and prohibit training on local PHI without explicit legal, ethics, and patient-facing consent.
Which AI scribes integrate best with Epic: Abridge, Suki, or Ambience?
As of 2025, Abridge, Suki, and Ambience Healthcare all offer strong Epic integrations with different strengths. Abridge excels at deep ambient capture and complex multisystem visits, Suki at voice-first commands plus scribing, and Ambience at real-time in-workflow prompts. Choice should depend on specialty mix, governance preferences, and desired workflow style.
How should we pilot and measure ROI for an Epic AI scribe integration project?
Run a 6–12 week pilot with 15–30 motivated clinicians across a few specialties. Start with a “shadow mode,” then compare pre/post metrics: active user rate, encounter coverage, time-to-sign, documentation accuracy and completeness, and clinician burnout scores. Include qualitative feedback to decide where to scale, limit, or decline adoption.
Past Review: